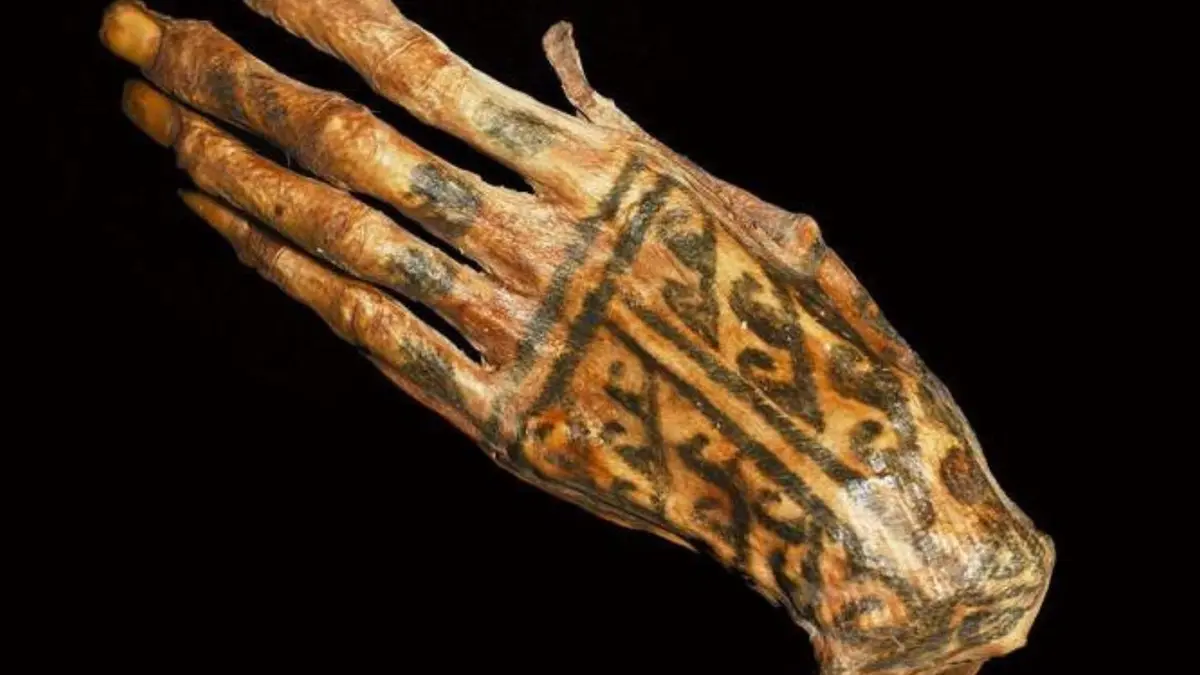
The art of tattooing has long served as a canvas for human expression, cultural identity, and spirituality. While the modern tattoo industry enjoys advanced technology and tools, the recent discovery of intricate 1,200-year-old tattoos on Peruvian mummies offers a remarkable glimpse into the dedication and artistry of ancient civilizations.
Using cutting-edge laser-stimulated fluorescence (LSF) technology, researchers have uncovered designs of exceptional precision that demonstrate the sophistication of pre-Hispanic tattoo practices.
A Technological Window Into the Past
The discovery of these tattoos was made possible by a team from the Chinese University of Hong Kong. They used advanced LSF technology to analyze the preserved remains of individuals from the Chancay culture, a pre-Hispanic civilization that thrived in present-day Peru around 900 CE.
Known for its mass production of ceramics, textiles, and metals, the Chancay culture has long fascinated archaeologists, but the artistry revealed in these tattoos provides a new dimension to understanding their society.
Laser-stimulated fluorescence works by emitting light onto a target, causing it to fluoresce and produce high-contrast images. In the case of the mummies, the preserved skin emitted fluorescence beneath the black tattoo ink, eliminating the effects of ink bleed and decay. This allowed researchers to uncover designs with astonishing clarity, showcasing linear details as fine as 0.1 to 0.2 millimeters wide.
Read : Woman Dies in China After Multiple Laser Treatments to Remove Birthmark
These findings challenge traditional views of ancient tattooing, emphasizing the deliberate skill and care involved in the process. Unlike pottery or textiles, tattoos on human skin are ephemeral and prone to fading over time.
Our @PNASNews paper introduces #LSF imaging to ancient tattoo analysis. In uncovering fine lines 0.1 -0.2mm thick, we reveal greater detail among thousand-year old tattoos on #Chancay mummies discovered in coastal #Peru. @CUHKScience @CUHKofficial #TattooTuesday #archaeology… pic.twitter.com/isjLpfy8sF
— Michael Pittman (@PalaeoPittman) January 14, 2025
The ability of LSF technology to recover such details reveals not only the cultural importance of tattoos in Chancay society but also the technical expertise of their artists.
Intricate Designs and Their Cultural Significance
The tattoos revealed by LSF technology are not only remarkable for their precision but also for their diversity and symbolism. The designs include geometric patterns, zoomorphic figures, and intricate linear motifs that reflect personal and cultural narratives.
Each tattoo appears to have been created with a deliberate hand, using pointed tools such as cactus needles or sharpened animal bones.
The artistry of these tattoos surpasses that of other Chancay artifacts, including pottery and textiles. This suggests that tattoos held a unique cultural significance, possibly tied to rites of passage, social status, or spiritual beliefs.
The intricate zoomorphic patterns, for example, could symbolize protective spirits or totems, while the geometric designs might represent cosmic or communal identities.

The process of tattooing in Chancay culture likely involved meticulous preparation and execution. The fine details of the artwork indicate that tattoo artists used tools even more refined than modern tattoo needles.
The cactus needles or animal bones employed in their craft demonstrate not only resourcefulness but also a deep understanding of the medium they worked with.
The cultural importance of these tattoos is further underscored by their presence on mummified remains, which were often preserved for ceremonial or commemorative purposes. The preservation of the skin, combined with the detailed artistry of the tattoos, suggests that these individuals may have held significant roles within their community.
Ancient Artistry Meets Modern Perspectives
The discovery of these tattoos not only enriches our understanding of ancient cultures but also invites reflection on the evolving perception of body art. In modern times, tattoos are often celebrated as a form of personal expression, yet they still carry varying connotations depending on cultural and generational contexts.
Interestingly, a separate study from the University of the Federal Armed Forces in Hamburg, Germany, highlights differences in attitudes toward tattoos across age groups.
While younger generations often embrace body art as a form of individuality and creativity, people over 50 tend to rate extreme tattoos as less attractive. This generational divide may stem from traditional stereotypes and societal norms that once associated tattoos with rebellion or marginalization.
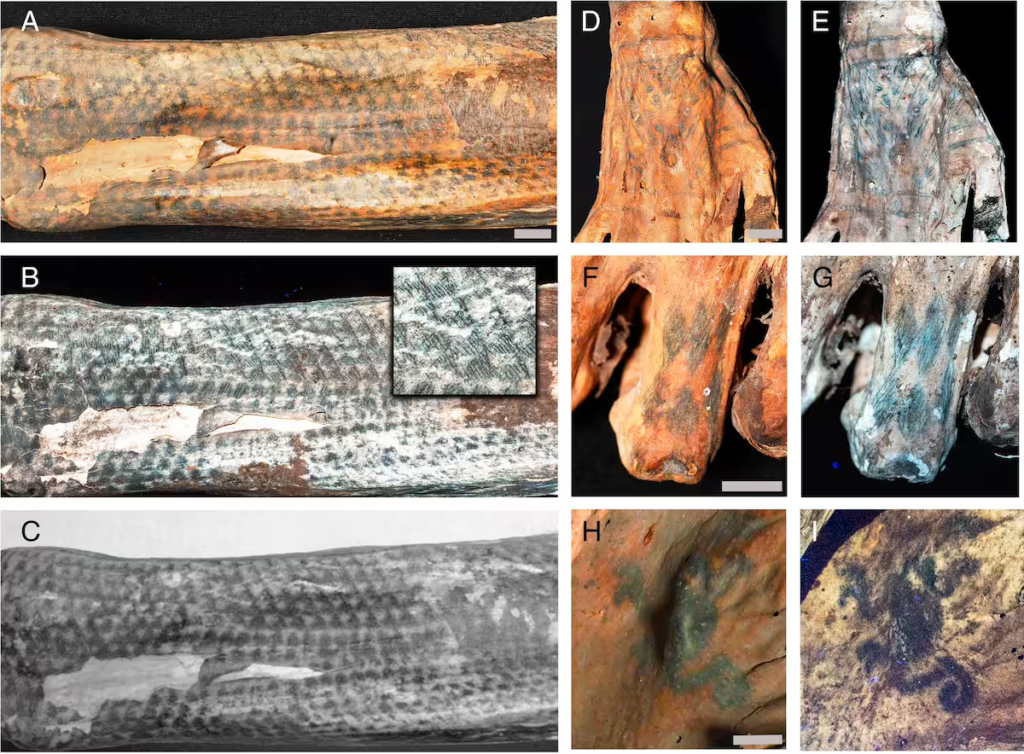
The contrast between ancient and modern perspectives on tattoos underscores their enduring relevance as a form of human expression. For the Chancay culture, tattoos were likely imbued with spiritual, social, or ceremonial significance, transcending mere decoration.
Today, tattoos continue to serve as powerful symbols of identity, though their meanings and societal acceptance have evolved over time.
The use of laser technology to uncover these ancient tattoos bridges the gap between past and present, allowing us to appreciate the artistry and cultural importance of body art across millennia.
The intricate designs etched onto the skin of 1,200-year-old mummies are a testament to the creativity and ingenuity of ancient tattoo artists, whose work endures as a legacy of human expression.
This groundbreaking discovery not only sheds light on the Chancay culture but also inspires a deeper appreciation for the universal human desire to leave a lasting mark on the world. Whether through traditional tools or advanced technology, the art of tattooing continues to connect us to our shared history and to each other.