Finland, a Nordic country located in Northern Europe, is a land of remarkable natural beauty, vibrant cities, and rich cultural heritage. Known for its vast forests, stunning lakes, and the enchanting Northern Lights, Finland offers a unique blend of modernity and tradition. From its picturesque landscapes to its innovative spirit, Finland is a country that captivates the imagination and invites exploration.
Table of Contents
Geography
Finland is situated in Northern Europe, sharing borders with Sweden to the west, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east. The country spans approximately 338,455 square kilometers, making it the eighth-largest country in Europe. Despite its size, Finland is sparsely populated, with vast areas of untouched wilderness.
The country’s landscape is characterized by over 188,000 lakes and 179,000 islands, earning it the nickname “The Land of a Thousand Lakes.” These water bodies are surrounded by dense forests, which cover about 74% of the country’s land area. The combination of lakes, forests, and rolling hills creates a stunning natural tapestry that changes with the seasons.
In the northernmost region of Finland lies Lapland, a place of extreme contrasts where the Midnight Sun shines for several weeks during summer, and the Northern Lights illuminate the dark winter skies. The geography of Finland is a testament to the raw beauty of nature, offering endless opportunities for outdoor activities and adventure.
States of Finland
Finland does not have states as some countries do. Instead, it is divided into 19 regions, known as “maakunnat” in Finnish. These regions are further subdivided into municipalities. Here are the 19 regions of Finland:
| No. | Region | Capital |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Åland Islands (Ahvenanmaa) | Mariehamn |
| 2 | Central Finland (Keski-Suomi) | Jyväskylä |
| 3 | Central Ostrobothnia (Keski-Pohjanmaa) | Kokkola |
| 4 | Kainuu | Kajaani |
| 5 | Kymenlaakso | Kouvola |
| 6 | Lapland (Lappi) | Rovaniemi |
| 7 | North Karelia (Pohjois-Karjala) | Joensuu |
| 8 | North Ostrobothnia (Pohjois-Pohjanmaa) | Oulu |
| 9 | Northern Savonia (Pohjois-Savo) | Kuopio |
| 10 | Ostrobothnia (Pohjanmaa) | Vaasa |
| 11 | Päijät-Häme | Lahti |
| 12 | Pirkanmaa | Tampere |
| 13 | Satakunta | Pori |
| 14 | South Karelia (Etelä-Karjala) | Lappeenranta |
| 15 | South Ostrobothnia (Etelä-Pohjanmaa) | Seinäjoki |
| 16 | Southern Savonia (Etelä-Savo) | Mikkeli |
| 17 | Uusimaa | Helsinki |
| 18 | Southwest Finland (Varsinais-Suomi) | Turku |
| 19 | Tavastia Proper (Kanta-Häme) | Hämeenlinna |
History
Finland’s history is a fascinating journey through time, marked by periods of independence, foreign rule, and cultural evolution. The earliest known inhabitants of Finland were hunter-gatherers who arrived around 8,500 BC, following the retreat of the Ice Age glaciers. These early settlers were followed by the Sámi people, indigenous to the region.
In the 12th century, Finland became a battleground for power between Sweden and Russia. The Swedish influence began to dominate, and by the late 13th century, Finland was fully integrated into the Kingdom of Sweden. This period saw the spread of Christianity and the establishment of Swedish as the dominant language in administration and education.
Finland declared its independence from Russia on December 6, 1917, following the Russian Revolution. The early years of independence were turbulent, marked by a civil war in 1918 between the “Reds” (leftists) and the “Whites” (conservatives). The Whites emerged victorious, leading to the establishment of a republican government. Despite the challenges, Finland maintained its sovereignty and developed into a modern welfare state through rapid industrialization and urbanization in the post-war period.
Capital City: Helsinki
Helsinki, the capital of Finland, is a dynamic and modern city that beautifully blends history, culture, and innovation. Founded in 1550 by King Gustav I of Sweden, Helsinki has grown from a small trading town to a vibrant metropolis and the largest city in Finland. Located on the southern coast, Helsinki overlooks the Gulf of Finland, providing a picturesque waterfront and an extensive archipelago of over 300 islands.
Known for its unique blend of modern architecture and historical buildings, Helsinki boasts iconic landmarks like the neoclassical Helsinki Cathedral, designed by Carl Ludvig Engel. The city’s cultural scene is vibrant, with numerous museums, theaters, and music venues, alongside a thriving design district that highlights Helsinki’s reputation as a hub of creativity and innovation.
Top Ten Most Famous Places in Finland
Finland, known for its stunning natural landscapes, vibrant cities, and unique cultural heritage, is a country that offers a diverse range of attractions. From the enchanting beauty of the Northern Lights to the architectural wonders of its cities, here are the top ten most famous places in Finland that showcase its charm and allure.
1. Helsinki

As the capital and largest city of Finland, Helsinki is a vibrant hub of culture and design. Visitors can explore the stunning architecture of the Helsinki Cathedral, the lively Market Square, and the unique structures at the Suomenlinna sea fortress, a UNESCO World Heritage site. The city’s rich history, coupled with its modern amenities, makes it an exciting destination for travelers.
2. Lapland

Lapland is known for its breathtaking natural beauty and is a prime location for experiencing the Northern Lights. This Arctic region is also famous for its winter activities, including skiing, snowshoeing, and dog sledding. Visitors can meet Santa Claus in Rovaniemi, the official hometown of Santa, making it a magical destination for families.
3. Rovaniemi

Rovaniemi, located in the heart of Lapland, serves as the gateway to Santa Claus Village. Here, visitors can enjoy a magical experience meeting Santa, crossing the Arctic Circle, and engaging in winter sports. The Arktikum Museum offers insights into Arctic culture and the history of Lapland, making Rovaniemi a must-visit for those seeking a unique Arctic experience.
4. Turku
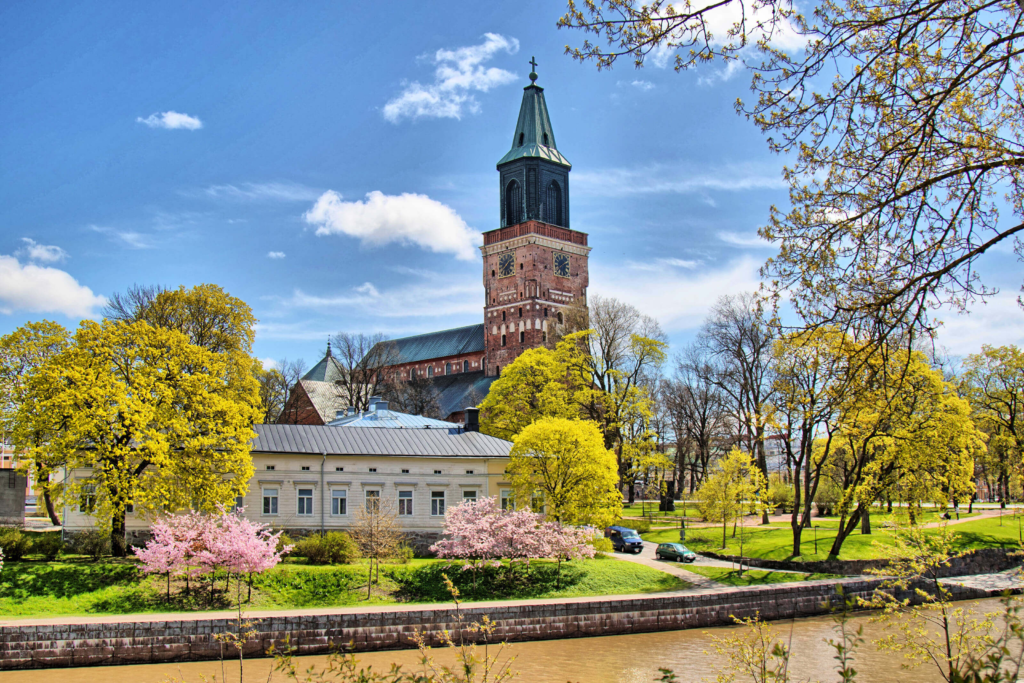

Turku, Finland’s oldest city, boasts a rich history and a picturesque setting along the Aura River. The Turku Castle and the Turku Cathedral are significant landmarks that reflect the city’s medieval past. The vibrant atmosphere of Turku, with its charming cafes, shops, and events, makes it a great place to explore Finnish culture and history.
5. Finnish Archipelago

The Finnish Archipelago, consisting of over 20,000 islands, is a paradise for nature lovers and outdoor enthusiasts. Visitors can enjoy island hopping, kayaking, and cycling through the stunning landscapes. The archipelago is home to charming villages, picturesque beaches, and unique wildlife, making it an ideal destination for a relaxing getaway.
6. Suomenlinna

Suomenlinna is a sea fortress located on a group of islands off the coast of Helsinki. This UNESCO World Heritage site is rich in history and offers beautiful landscapes, museums, and walking paths. Visitors can explore the fortifications, enjoy picnics in the parks, and learn about the fortress’s significance in Finnish history.
7. Porvoo

Porvoo is a charming medieval town known for its well-preserved wooden houses and cobblestone streets. The picturesque old town, with its vibrant buildings and beautiful riverside views, attracts visitors looking to experience Finnish heritage. The Porvoo Cathedral and various artisan shops add to the town’s charm and cultural significance.
8. Saimaa Lake

Saimaa Lake, the largest lake in Finland, is known for its stunning scenery and unique wildlife, including the endangered Saimaa ringed seal. Visitors can enjoy activities like boating, fishing, and hiking in the surrounding national parks. The area offers numerous cottages and resorts, making it an excellent destination for a peaceful retreat in nature.
9. Levi

Levi is a popular ski resort located in Finnish Lapland, offering excellent skiing and snowboarding opportunities. In addition to winter sports, visitors can enjoy activities like snowmobiling, ice fishing, and experiencing the local Sámi culture. The breathtaking winter landscapes and cozy accommodations make Levi a top destination for winter enthusiasts.
10. Koli National Park

Koli National Park is renowned for its stunning views, hiking trails, and beautiful landscapes. The park features the iconic Koli Hill, which offers breathtaking panoramas of Lake Pielinen and the surrounding forests. Visitors can explore various trails, enjoy outdoor activities, and experience the tranquility of Finland’s nature, making it a haven for nature lovers.
Culture
Finnish culture is deeply rooted in the country’s natural environment, history, and traditions. The Finnish people have a strong connection to nature, which is reflected in their love for outdoor activities such as hiking, skiing, and ice fishing. The concept of “sisu,” a unique Finnish term that embodies resilience, determination, and courage, is a fundamental part of the national identity.
The sauna is an integral part of Finnish culture, with over two million saunas in the country. It is a place for relaxation, socializing, and even conducting business. The sauna tradition dates back thousands of years and continues to be an essential aspect of Finnish life.
Finnish folklore is rich with mythology and legends, with the Kalevala being the most famous national epic. Compiled by Elias Lönnrot in the 19th century, the Kalevala is a collection of ancient Finnish songs and poems that tell the stories of mythical heroes and gods. These tales have had a significant influence on Finnish literature, art, and music.
Language
Finnish is the official language of Finland and is spoken by the majority of the population. It belongs to the Finno-Ugric language family, which is distinct from the Indo-European languages spoken in most of Europe. The Finnish language is known for its complex grammar and extensive use of vowel harmony.
Swedish is also an official language in Finland, spoken by a minority of the population, particularly in coastal areas and the Åland Islands. Finland’s bilingualism is a testament to its historical ties with Sweden and its commitment to preserving linguistic diversity.
The Finnish education system places a strong emphasis on language learning, and many Finns are proficient in English, which is widely taught in schools. This multilingualism reflects Finland’s open and inclusive approach to communication and cultural exchange.
Economy
Finland has a highly developed economy that is characterized by innovation, technology, and a strong welfare state. The country consistently ranks high in global competitiveness, education, and quality of life indices. Finland’s economic success can be attributed to its focus on education, research and development, and a robust social security system.
The technology sector is a significant driver of Finland’s economy, with companies like Nokia playing a crucial role in the global telecommunications industry. Finland is also a leader in renewable energy, with a commitment to reducing carbon emissions and promoting sustainable practices.
The Finnish economy is diversified, with key industries including manufacturing, electronics, forestry, and information technology. Finland’s forests are a valuable natural resource, supporting a thriving timber and paper industry. The country’s commitment to sustainability ensures that these resources are managed responsibly.
Education
Finland is renowned for its education system, which is considered one of the best in the world. The Finnish approach to education emphasizes equity, creativity, and student well-being. Teachers in Finland are highly trained and respected professionals, and the education system is designed to foster critical thinking and lifelong learning.
One of the hallmarks of Finnish education is its focus on personalized learning. Class sizes are small, allowing teachers to provide individualized attention and support to students. The curriculum is flexible, encouraging students to pursue their interests and develop their unique talents.
Finland’s commitment to education extends to higher education, with several world-class universities and research institutions. Finnish universities are known for their high academic standards and innovative research, attracting students and scholars from around the globe.
Healthcare
Finland boasts a comprehensive healthcare system that provides high-quality medical services to all residents. The country’s healthcare system is based on universal coverage, ensuring that everyone has access to essential health services regardless of their financial situation.
The Finnish healthcare system is funded through taxes and operates on a decentralized model, with municipalities responsible for providing primary care services. Specialized care is provided by regional hospital districts, ensuring that patients receive the appropriate level of care for their needs.
Preventive care and health promotion are key components of the Finnish healthcare system. Public health initiatives focus on promoting healthy lifestyles, preventing chronic diseases, and reducing health disparities. Finland’s commitment to healthcare has resulted in high life expectancy and low infant mortality rates.
Social Welfare
Finland is known for its strong social welfare system, which provides a safety net for all citizens. The Finnish welfare state is built on the principles of equality, solidarity, and social justice. It includes comprehensive social security programs, such as unemployment benefits, pensions, and child allowances, designed to support individuals and families throughout their lives.
Family policies in Finland are particularly notable, with generous parental leave, subsidized childcare, and financial support for families with children. These policies aim to promote work-life balance and ensure that all children have the opportunity to thrive.
The Finnish welfare system also includes robust housing policies, ensuring that everyone has access to affordable and decent housing. Social services provide support for vulnerable populations, including the elderly, people with disabilities, and those facing financial difficulties.
Environment and Sustainability
Finland is a global leader in environmental protection and sustainability. The country’s commitment to preserving its natural resources and reducing its environmental footprint is evident in its policies and practices. Finland has set ambitious targets for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and increasing the use of renewable energy.
Forestry is a critical industry in Finland, and sustainable forest management practices are essential to maintaining the health of the country’s forests. Finland has implemented strict regulations to ensure that logging is conducted in an environmentally responsible manner, protecting biodiversity and preventing deforestation.
Finland’s cities are known for their green spaces and clean air, with urban planning focused on sustainability and quality of life. Public transportation is efficient and well-developed, reducing the reliance on private cars and minimizing traffic congestion and pollution.
Tourism
Finland’s natural beauty and unique cultural experiences make it a popular destination for tourists. The country’s diverse landscapes offer something for every traveler, from the rugged wilderness of Lapland to the picturesque lakes and forests of the Lakeland region.
One of the most sought-after experiences in Finland is witnessing the Northern Lights. The best time to see this natural phenomenon is during the winter months in Lapland, where the dark skies provide the perfect backdrop for the dazzling display of colors.
The Midnight Sun is another unique natural phenomenon that attracts visitors to Finland. During the summer months, the sun does not set for several weeks in the northern parts of the country, creating a magical experience of endless daylight.
Finnish culture and traditions are also a significant draw for tourists. Visitors can experience the Finnish way of life by staying in traditional log cabins, participating in sauna rituals, and sampling local cuisine. Festivals and events, such as the Midsummer celebration and the Savonlinna Opera Festival, offer a glimpse into Finland’s rich cultural heritage.
Cuisine
Finnish cuisine is characterized by its simplicity, freshness, and use of local ingredients. Traditional Finnish dishes often feature fish, game, and vegetables, reflecting the country’s natural bounty. Rye bread, salmon, and berries are staples of the Finnish diet, providing both nutrition and flavor.
One of the most iconic Finnish foods is the “karjalanpiirakka,” a Karelian pasty made with a rye crust and filled with rice porridge. These pasties are typically served with “munavoi,” a mixture of butter and chopped boiled eggs.
Salmon is a popular ingredient in Finnish cuisine, prepared in various ways, including smoked, grilled, and served in soups. “Lohikeitto,” a creamy salmon soup, is a beloved Finnish dish that showcases the delicate flavor of the fish.
Berries, such as lingonberries, blueberries, and cloudberries, are abundant in Finland and are used in a variety of dishes, from desserts to sauces. “Leipäjuusto,” also known as Finnish squeaky cheese, is often served with cloudberry jam, creating a delightful combination of flavors.
Top Eight Most Famous Food of Finland







Innovation and Technology
Finland is renowned for its innovation and technological advancements. The country has a strong culture of research and development, supported by a well-educated workforce and a robust startup ecosystem. Finland’s commitment to innovation has resulted in numerous breakthroughs in various fields, from telecommunications to renewable energy.
The technology sector is a cornerstone of Finland’s economy, with a particular focus on information and communications technology (ICT). Companies like Nokia have played a significant role in shaping the global telecommunications industry, and Finland continues to be a leader in mobile technology and digital solutions.
Finland’s education system plays a crucial role in fostering innovation, with a strong emphasis on STEM (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics) education. Finnish universities and research institutions are at the forefront of cutting-edge research, contributing to advancements in fields such as artificial intelligence, biotechnology, and environmental science.
Conclusion
Finland is a country that seamlessly blends natural beauty, rich cultural heritage, and technological innovation. From its stunning landscapes of lakes and forests to its vibrant cities and resilient people, Finland offers a unique and captivating experience for visitors and residents alike. The country’s commitment to education, sustainability, and social welfare reflects its forward-thinking approach and dedication to improving the quality of life for all. Whether exploring the wilderness of Lapland, experiencing the cultural vibrancy of Helsinki, or embracing the Finnish way of life, there is no shortage of reasons to fall in love with Finland.
let’s enjoy few years on earth with peace and happiness….✍🏼🙏

