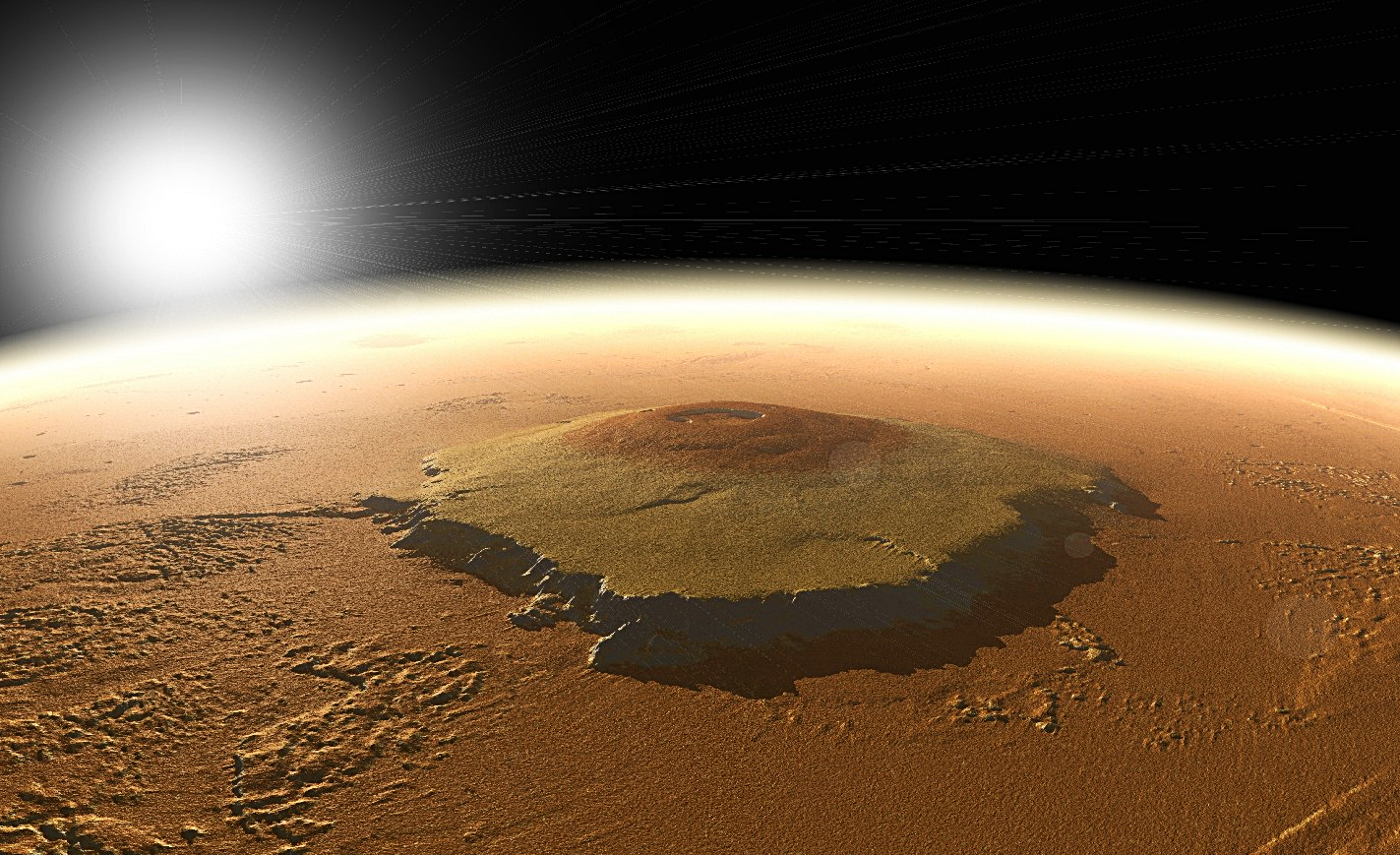
Olympus Mons, a magnificent shield volcano on Mars, reigns as the tallest mountain in the solar system, towering above all other planetary peaks. This colossal structure, standing approximately 22 kilometers (13.6 miles) high, far exceeds the height of Mount Everest, Earth’s tallest mountain.
Olympus Mons is not just an impressive landmark; it is a significant geological feature that provides insights into the volcanic history of Mars and the nature of planetary formation in our solar system.
In this blog, we will explore the formation and characteristics of Olympus Mons, its environmental context, the scientific exploration it has inspired, its potential for future exploration, and its role in our understanding of Mars and beyond.
Formation and Geological Characteristics of Olympus Mons
The formation of Olympus Mons is a fascinating process that reveals much about Mars’s geological history. Olympus Mons is classified as a shield volcano, characterized by its broad, gently sloping profile, which is a result of the eruption of low-viscosity basaltic lava. This type of volcano is different from the steeper stratovolcanoes found on Earth, such as Mount St. Helens or Mount Fuji.
Read : China to Launch Mars Mission in 2028, Aims to Bring Back 600 gm Soil
Geologists believe that Olympus Mons began forming over 200 million years ago during a period of significant volcanic activity on Mars. Unlike Earth, where tectonic plate movements can cause the destruction of volcanoes, the lack of plate tectonics on Mars allowed Olympus Mons to grow continuously over millions of years.
Read : Mysterious ‘Hole’ on the Flank of an Ancient Volcano on Mars Could Shelter Humans: Research
Lava flowed freely from the volcano, building up layers upon layers of basalt rock, contributing to its immense height and width.
One of the most remarkable features of Olympus Mons is its caldera, a large depression at the summit formed by the collapse of the volcano after a series of explosive eruptions.
The caldera measures about 80 kilometers (50 miles) in diameter and contains several overlapping craters, indicating multiple eruptive events over time.
The steep cliffs surrounding the caldera, known as the scarp, rise up to 7 kilometers (4.3 miles) above the surrounding plains, creating a dramatic landscape that is both awe-inspiring and scientifically significant.
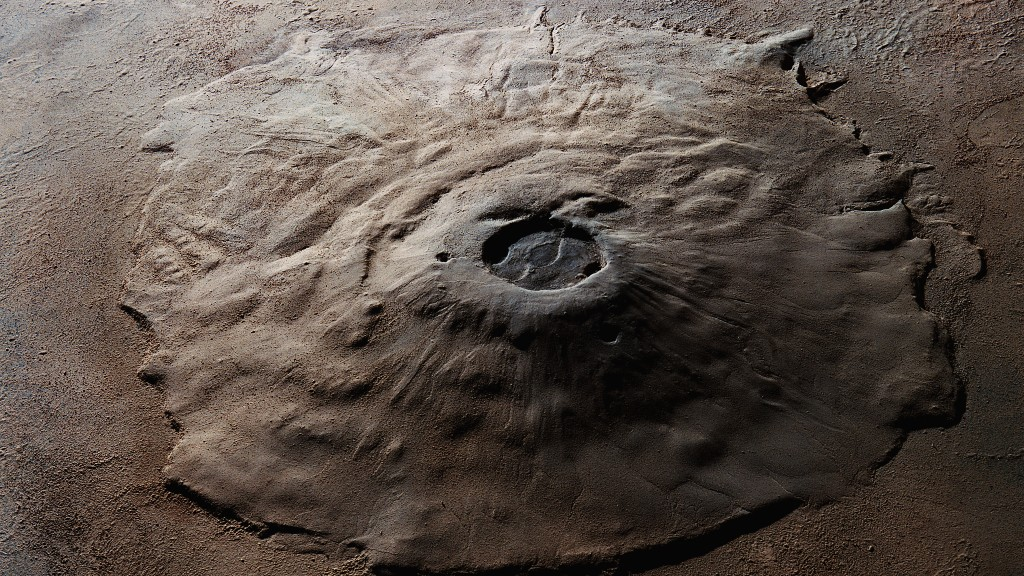
In addition to its impressive height, Olympus Mons spans an astounding diameter of approximately 600 kilometers (373 miles), making it the largest volcano in the solar system. The sheer size of Olympus Mons and its unique geological features have made it a subject of intense scientific study and fascination.
Atmospheric and Environmental Context
Understanding the environmental conditions on Mars is crucial to comprehending the processes that shaped Olympus Mons. Mars has a thin atmosphere composed primarily of carbon dioxide, with surface pressure less than 1% of that on Earth. This thin atmosphere plays a significant role in how volcanic eruptions occur and how lava flows behave.
The low atmospheric pressure on Mars allows lava to flow more freely than it would on Earth, contributing to the broad, gently sloping profile of Olympus Mons.
The lack of significant atmospheric erosion means that the mountain’s features are well-preserved, providing a valuable record of Martian volcanic activity.
Mars’s climate is marked by extreme temperature variations, with surface temperatures averaging around -63 degrees Celsius (-81 degrees Fahrenheit). These harsh conditions pose challenges for exploration and habitation but also influence the geological processes that shape the planet.
The cold temperatures on Mars lead to the formation of frost and polar ice caps, further contributing to the unique environmental conditions observed on the planet.
Research indicates that, despite its extreme conditions, Olympus Mons may still exhibit signs of volcanic activity, albeit on a smaller scale compared to its formative years.
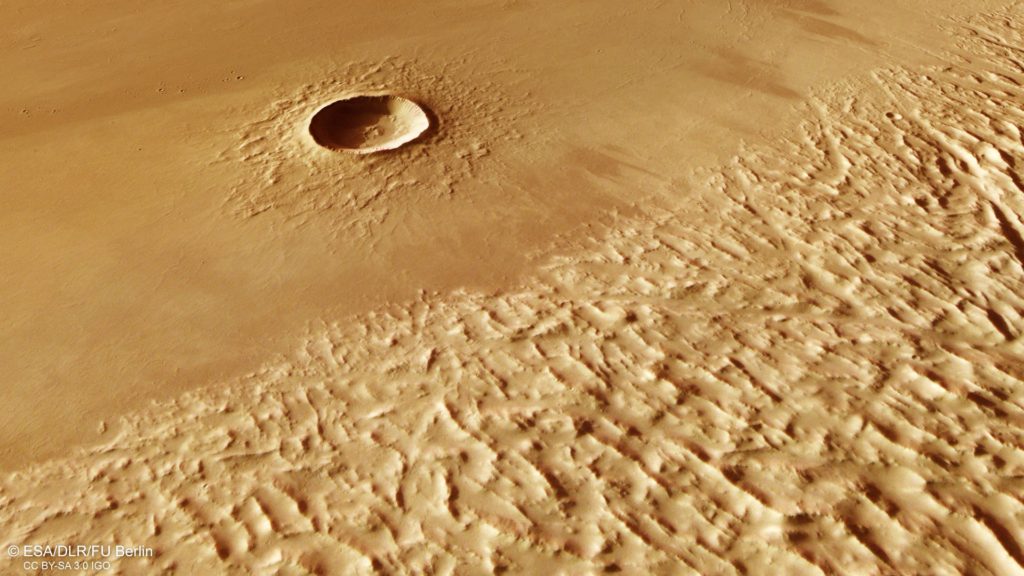
Recent studies have suggested that some geological features around Olympus Mons, such as lava flows and fissures, may indicate that the volcano is not entirely extinct. Monitoring Olympus Mons could provide insights into ongoing geological processes on Mars and help scientists understand the planet’s volcanic history better.
Scientific Exploration and Discoveries
The exploration of Olympus Mons has been a focal point for Mars missions since the first images of the mountain were captured by the Viking orbiters in the 1970s.
Subsequent missions, such as the Mars Global Surveyor and Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, have provided high-resolution images and detailed geological maps of the region, enhancing our understanding of its structure and formation.
Scientists study Olympus Mons not only to learn about Martian geology but also to gain insights into volcanic activity on other planets. By comparing the characteristics of Olympus Mons with those of Earth’s volcanoes, researchers can better understand the differences in volcanic activity across the solar system.
The study of Olympus Mons is also significant for astrobiology. Understanding the geological history of Mars, including its volcanic activity, can provide clues about the planet’s past climate and the potential for life.
If Mars was once warmer and wetter, it may have been capable of supporting microbial life. The exploration of Olympus Mons, therefore, holds the potential for discovering evidence of past life and understanding the evolution of Martian environments.
The data collected from Mars missions has led to exciting discoveries regarding the geology of Olympus Mons. For instance, researchers have found that the surface of the volcano is covered with numerous lava flow features and volcanic pits, indicating a rich history of eruptions.

The presence of these geological features suggests that the volcano has experienced a long and complex volcanic history, making it a valuable site for understanding the evolution of volcanic activity on Mars.
Potential for Future Exploration
As space agencies and private companies continue to plan missions to Mars, Olympus Mons is expected to be a key target for exploration. Future missions could include landers and rovers designed to study the mountain’s geology, atmosphere, and potential resources.
The enormous size of Olympus Mons presents unique challenges and opportunities for human exploration and habitation. Its vast surface area could provide a platform for constructing habitats and research stations, making it an ideal location for studying the Martian environment up close.
Additionally, the geological features of Olympus Mons may contain valuable resources, such as water ice and minerals, essential for sustaining human life. The presence of water ice, in particular, would be critical for any future human missions, as it could be used for drinking water, agriculture, and even rocket fuel.
Technological advancements in robotics and space exploration will enable more detailed studies of Olympus Mons in the coming years. The development of sophisticated landers and rovers equipped with advanced scientific instruments could allow researchers to analyze the composition of the rocks and soils in and around Olympus Mons.
Such missions could yield valuable data about the volcano’s eruptive history and the conditions that prevailed on Mars during its formation.
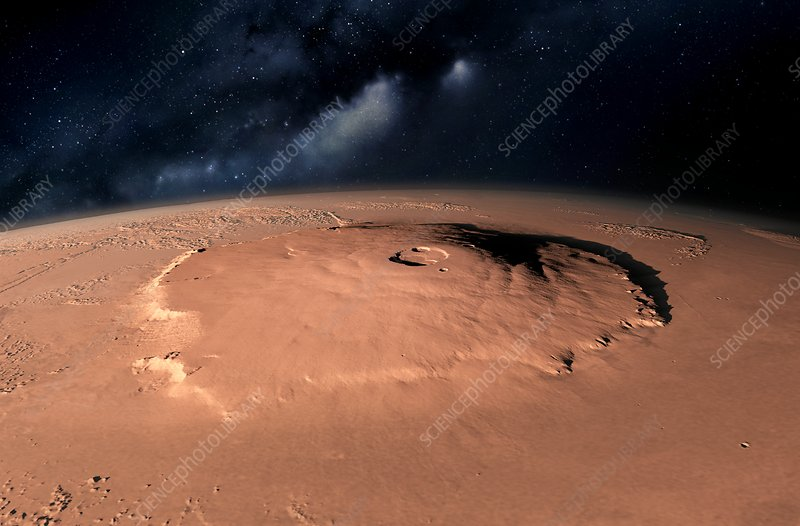

The exploration of Olympus Mons also raises important questions about the potential for human settlement on Mars. As we consider the possibilities of colonizing the Red Planet, understanding the geological and environmental characteristics of Olympus Mons will be essential. The unique features of the mountain may provide resources and insights that could support human life in the harsh Martian environment.
Olympus Mons stands as a testament to the incredible geological processes that have shaped Mars over millions of years. As the tallest mountain in the solar system, it offers a unique perspective on volcanic activity, planetary evolution, and the potential for life beyond Earth.
Ongoing exploration of this majestic volcano will undoubtedly continue to enhance our understanding of Mars and its history, paving the way for future human exploration and habitation.
As we look to the future, the mysteries of Olympus Mons will inspire generations of scientists, explorers, and dreamers alike.
With advancements in technology and a growing interest in Mars exploration, we are on the cusp of unlocking the secrets of Olympus Mons and furthering our knowledge of the Red Planet.
This remarkable mountain serves as a reminder of the wonders of our solar system and the potential for discovery that awaits us beyond our home planet.

