A bizarre case in Singapore has shocked medical experts and the public alike. A 30-year-old man had to undergo emergency surgery after speed eating 7-pound burger during a competition.
The massive intake of food caused his stomach to stretch beyond its limits, leading to severe health complications. This rare but serious condition serves as a reminder of the dangers of excessive food consumption, especially in extreme eating competitions.
The Risks of Extreme Eating Competitions
Competitive eating has gained popularity in recent years, with contestants challenging themselves to consume large amounts of food in a short period. However, what many fail to realize is the significant strain such activities put on the digestive system.
The human stomach has a normal capacity of approximately 1 to 1.5 liters, though it can stretch to accommodate more food. In extreme cases, as seen in this Singaporean man’s ordeal, the stomach can stretch so much that it affects surrounding organs, leading to potentially life-threatening complications.
Doctors reported that the man’s stomach expanded far beyond its normal size, pressing against his pancreas and causing him unbearable pain. A CT scan revealed that his stomach was packed with undigested food, preventing normal digestion and blood circulation. If left untreated, this condition could have resulted in stomach rupture, sepsis, or even death.
Read : Envy Over Promotion Woman Poisons Co-Worker at Textile Factory in Brazil
The case highlights the severe consequences of excessive eating, particularly in short bursts. Unlike gradual overeating, speed eating does not allow the digestive system to function properly, resulting in a dangerous buildup of food.
Read : Japan is Selling the Electric Spoon for “Healthier Eating”: Here’s How It Works
Experts warn that participants in eating competitions are at risk of developing acute gastric dilation, a condition where the stomach becomes overstretched and struggles to contract back to its normal size.
The Medical Consequences of Overeating
While most people occasionally overeat, excessive consumption can have immediate and long-term effects on health. In the case of the 30-year-old Singaporean man, the speed at which he consumed the burger played a crucial role in his medical emergency. The body needs time to break down food, and when a large quantity is consumed rapidly, digestion slows down significantly.
One of the biggest dangers of overeating is stomach rupture, which occurs when the stomach walls can no longer withstand the pressure of excessive food. This can lead to food leaking into the abdominal cavity, causing infections and inflammation. In severe cases, emergency surgery is required to remove the undigested food and repair any damage to the stomach.
Other complications linked to overeating include acid reflux, where stomach acid travels back up into the esophagus, causing discomfort and long-term damage to the digestive tract.
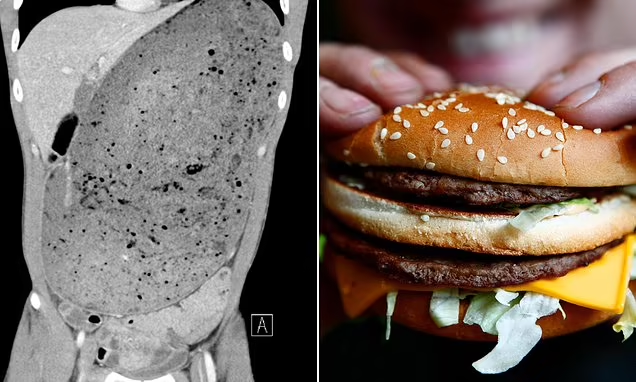
Additionally, overeating can put a strain on the cardiovascular system, increasing the risk of high blood pressure, heart disease, and diabetes. In the Singaporean man’s case, his body showed signs of extreme stress, including elevated infection markers in his blood.
Beyond the immediate health risks, overeating can also contribute to long-term medical conditions. Obesity, a major health concern worldwide, is often linked to unhealthy eating patterns, including binge eating. Over time, excessive food intake can lead to metabolic disorders, insulin resistance, and an increased risk of certain cancers.
Understanding Binge Eating Disorder
Binge eating disorder (BED) is a serious medical condition characterized by the consumption of large amounts of food in a short period, often accompanied by a loss of control over eating habits. While not all cases of overeating result in medical emergencies, repeated episodes can have serious physical and psychological consequences.
People with BED often consume food rapidly and continue eating even when they feel full. This pattern is different from normal overeating, as individuals with the disorder experience extreme distress and guilt after their eating episodes. The disorder is more common among women but can affect men as well.
Several factors contribute to binge eating disorder, including genetic, psychological, and environmental influences. Studies suggest that people with a family history of eating disorders are more likely to develop BED.
Additionally, individuals who experience high levels of stress or anxiety may turn to food as a coping mechanism, leading to repeated binge-eating episodes.

The consequences of BED extend beyond weight gain. Many individuals with the disorder struggle with obesity, high cholesterol, and cardiovascular diseases.
Furthermore, binge eating is linked to an increased risk of mental health issues, including depression and anxiety. The emotional toll of BED can be severe, leading to social isolation and a decreased quality of life.
Understanding and addressing BED requires a multi-faceted approach, including behavioral therapy, dietary changes, and medical intervention in severe cases.
Unlike other eating disorders, BED does not always involve purging behaviors, making it harder to diagnose and treat. However, early intervention can help individuals regain control over their eating habits and prevent long-term health complications.
The case of the Singaporean man who underwent surgery after speed eating a 7-pound burger serves as a stark reminder of the dangers of excessive food consumption.
While eating competitions may seem like harmless fun, they pose serious risks to participants’ health. Overeating, whether in a competitive setting or due to an eating disorder, can lead to severe medical conditions that require urgent treatment.
Understanding the consequences of overeating and taking steps to promote healthier eating habits can help prevent similar medical emergencies. Whether it’s avoiding speed-eating competitions or seeking treatment for binge eating disorder, prioritizing digestive health is crucial for overall well-being.