China recently reported the detection of a new Mpox variant, Clade Ib, sparking concern among global health authorities. The variant, first identified in a foreign traveller with a history of travel and residence in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), has resulted in a cluster outbreak. Chinese health authorities are closely monitoring the situation to prevent further spread and ensure public safety.
Discovery of the New Mpox Variant in China
The new Mpox variant, Clade Ib, came to light after a foreign traveller entering China exhibited symptoms consistent with the viral infection.
The individual had a history of travel and residence in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, where Mpox is endemic. Following the detection of the variant, Chinese health authorities identified four additional cases among individuals who had close contact with the initial patient.
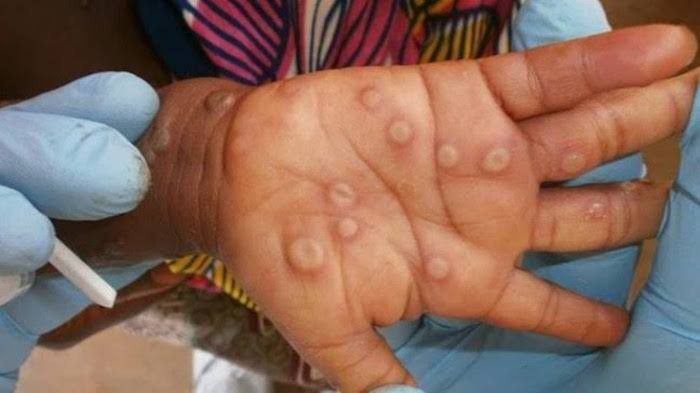
Mpox, also known as Monkeypox, spreads through close contact and is characterized by flu-like symptoms, skin rashes, and pus-filled lesions. While most cases are mild, the disease can occasionally result in severe complications and even fatalities. The symptoms among the identified cases in China have been reported as mild, primarily involving skin rashes and blisters.
Read : China Discovers Vast Copper Deposit in Tibetan Plateau
This discovery highlights the importance of global vigilance and proactive measures to manage the spread of infectious diseases. The detection of the Clade Ib variant, which appears to spread more readily through routine close contact, including sexual contact, underlines the need for enhanced surveillance and public health strategies.
Global Context and Spread of Mpox
Mpox has been a recurring concern in recent years, particularly in Central and West Africa, where the virus is endemic. The Democratic Republic of the Congo has been a hotspot for outbreaks, with the endemic strain, Clade I, causing significant challenges for local health systems. However, the Clade Ib variant represents a new mutation with potentially increased transmissibility.
Read : Chinese Scientists Create Mutant Ebola Virus in the Lab That Causes Horrible Symptoms
The World Health Organization (WHO) declared Mpox a global public health emergency in August 2022, following a significant outbreak in the DRC that spread to neighboring countries, including Burundi, Kenya, Rwanda, and Uganda. This declaration emphasized the urgent need for international cooperation in tracking and containing the virus.
The Clade Ib variant’s ability to spread more easily through routine close contact has raised alarms about its potential to cause widespread outbreaks beyond Africa. This is particularly concerning in densely populated areas and regions with limited healthcare infrastructure.
China’s identification of the Clade Ib variant highlights the interconnected nature of global health. As international travel resumes in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, the risk of infectious diseases crossing borders has increased. This underscores the necessity for countries to implement robust health screening measures for travellers and goods entering their territories.
China’s Response to the Mpox Outbreak
China has implemented a range of measures to address the Mpox outbreak and prevent further transmission. The National Health Commission has classified Mpox as a Category B infectious disease, allowing authorities to take emergency actions such as restricting gatherings, suspending work and school, and sealing off affected areas.
In response to the recent cases, Chinese authorities have intensified monitoring efforts at entry points, including airports and seaports, to identify potential cases among incoming travellers. Public health campaigns have been launched to educate citizens about the symptoms of Mpox and the importance of reporting suspected cases.
Additionally, the government is conducting contact tracing to identify and isolate individuals who may have been exposed to the virus. This approach aims to break the chain of transmission and limit the spread of the Clade Ib variant.
Collaboration with international health organizations, such as the WHO, is also a critical component of China’s response strategy. Sharing data and insights about the Clade Ib variant can aid in developing targeted interventions and ensuring a coordinated global effort to combat the virus.
The detection of the Clade Ib variant serves as a stark reminder of the importance of investing in healthcare infrastructure and research. Strengthening disease surveillance systems, improving diagnostic capabilities, and enhancing access to vaccines and treatments are essential steps in preparing for future outbreaks.
As Mpox continues to spread globally, the lessons learned from this outbreak can inform strategies to address similar challenges in the future. The emergence of new variants underscores the need for ongoing vigilance and collaboration to protect public health on a global scale.