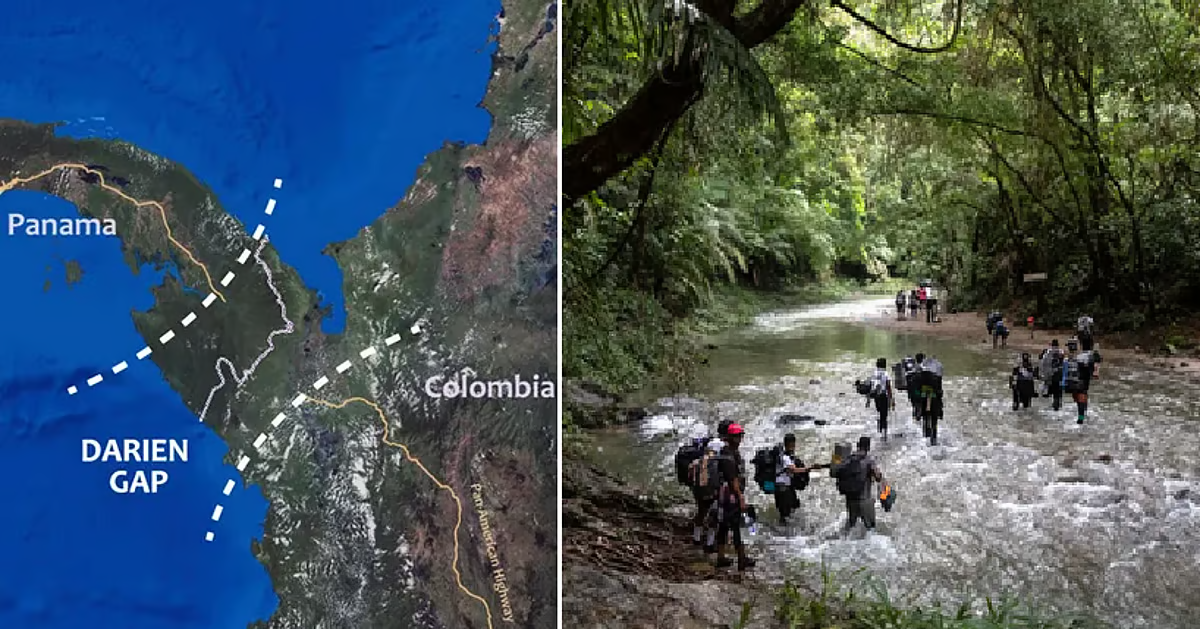
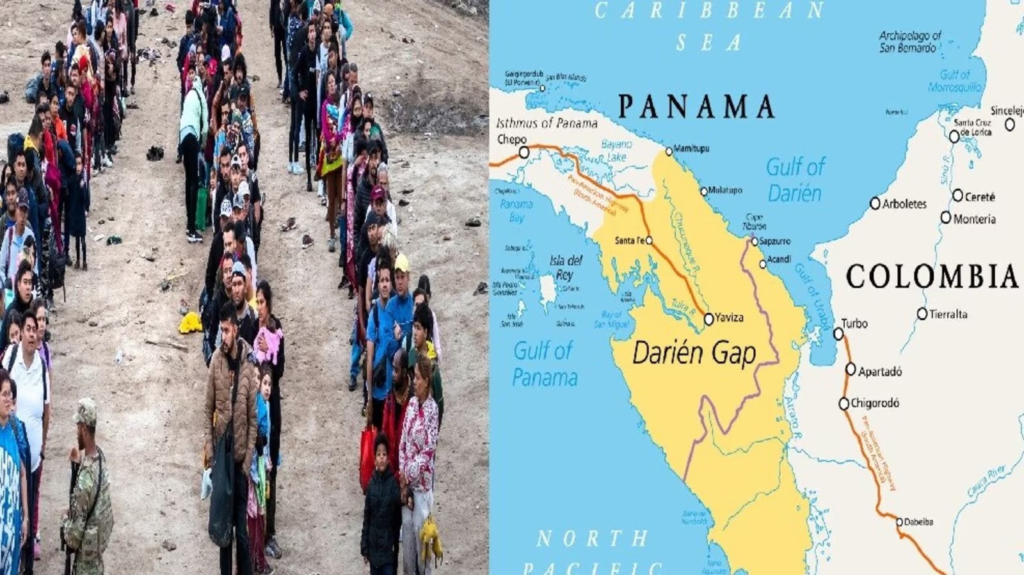
The Darien Gap, a dense and perilous jungle spanning 97 kilometers between Colombia and Panama, has become one of the most dangerous migration routes in the world.
This roadless region, once avoided due to its harsh terrain and lawlessness, is now a crucial passage for thousands of migrants attempting to reach the United States. As global migration patterns shift and visa restrictions tighten, many are forced to take this treacherous path despite the severe risks involved.
The Perils of the Darien Gap
The Darien Gap is a natural barrier that separates South America from Central America, making it the only break in the Pan-American Highway, a road network stretching from Alaska to Argentina.
The area is infamous for its extreme environment, consisting of dense rainforest, muddy swamps, steep mountains, and fast-moving rivers. These natural obstacles make the crossing physically demanding, with migrants enduring weeks of trekking through dangerous terrain with minimal supplies.
One of the most significant hazards is the jungle’s wildlife, which includes venomous snakes, jaguars, and disease-carrying insects. Many migrants suffer from dehydration, malnutrition, and infections due to exposure to the elements.
Additionally, the lack of infrastructure means that those who fall ill or are injured have little to no access to medical help. Deaths due to exhaustion, drowning, or animal attacks are common, and bodies are often left unburied due to the region’s remoteness.
Beyond the natural dangers, the Darien Gap is also a hotspot for crime and violence. The region is controlled by smuggling networks, drug cartels, and armed groups that exploit vulnerable migrants. Reports indicate that criminal organizations demand payments for safe passage, but often rob, kidnap, or abandon migrants instead.
Women and children are especially at risk, with humanitarian organizations reporting widespread sexual violence along the route. Medecins Sans Frontieres (Doctors Without Borders) recorded 676 cases of sexual assault in 2023 alone, and hundreds more have been reported in early 2024.
Read : 130 Indians Who Took The Donkey Route Deported from Panama
Migrants who survive the journey often arrive in Panama with severe injuries and trauma. Many are stranded in overcrowded shelters that lack basic necessities like food, clean water, and medical aid.
The increasing number of people using the Darien Gap as a migration corridor has put a strain on local resources, leading to a humanitarian crisis. Indigenous communities living along the route are overwhelmed, and environmental damage, including deforestation and pollution, has worsened due to the growing number of crossings.
The ‘Donkey Route’: A Desperate Journey to the US
Migrants from around the world, including Venezuela, Haiti, Ecuador, Bangladesh, Pakistan, and India, use what is known as the ‘donkey route’ to reach the United States. This involves traveling to Central American countries with easier visa policies, such as Panama, Costa Rica, El Salvador, and Guatemala, before attempting to cross into Mexico and eventually the US.
For many Indians, the journey starts with a legal flight to a South or Central American country. From there, they rely on human smugglers, known as coyotes, to navigate the treacherous path.
These smugglers charge thousands of dollars for the journey, often promising safe passage but abandoning migrants in life-threatening conditions. Despite the risks, the ‘donkey route’ has become an increasingly popular method due to the strict visa restrictions imposed by the US on travelers from countries with high migration rates.
The scale of migration through the Darien Gap has increased dramatically in recent years. In 2023, over 5.2 lakh (520,000) migrants made the crossing, more than double the number from the previous year.
By mid-2024, over 3 lakh (300,000) people had already undertaken the journey, although increased enforcement efforts have led to a slight decline. A decade ago, only a few thousand migrants attempted this route annually, highlighting the rapid growth of this migration crisis.
As more migrants attempt the journey, the dangers continue to escalate. Organized crime groups have turned the Darien Gap into a profitable human trafficking corridor, with Colombia’s Gulf Clan reportedly earning $57 million from migrant crossings in just the first 10 months of 2023.
These criminal organizations have established a well-coordinated smuggling network, ensuring a steady flow of migrants while profiting from their desperation.
Humanitarian and Political Responses to the Crisis
The humanitarian crisis in the Darien Gap has drawn international attention, with organizations like the United Nations, Red Cross, and Doctors Without Borders calling for urgent intervention.
Aid groups provide food, medical care, and shelter to those who survive the journey, but resources remain inadequate given the scale of the crisis. Overcrowded refugee camps in Panama struggle to accommodate the influx of migrants, while limited government funding has hindered efforts to improve living conditions.
Social media misinformation, often spread by smugglers, has worsened the situation by giving migrants false hope about the ease of crossing.
Many are lured into making the journey based on misleading information, only to find themselves trapped in one of the most hostile environments in the world. Some migrants turn back after witnessing the horrors of the jungle, while others push forward, hoping for a better future in the US.
The US government has taken steps to curb illegal migration, increasing border security and deportation efforts. The recent deportation of 104 Indian migrants, who were handcuffed and shackled for nearly 24 hours on their flight back to India, highlights the strict immigration policies under President Joe Biden’s administration.
Former President Donald Trump’s stance on illegal immigration remains a key political issue, and discussions on border security have intensified, especially in light of his recent call with Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
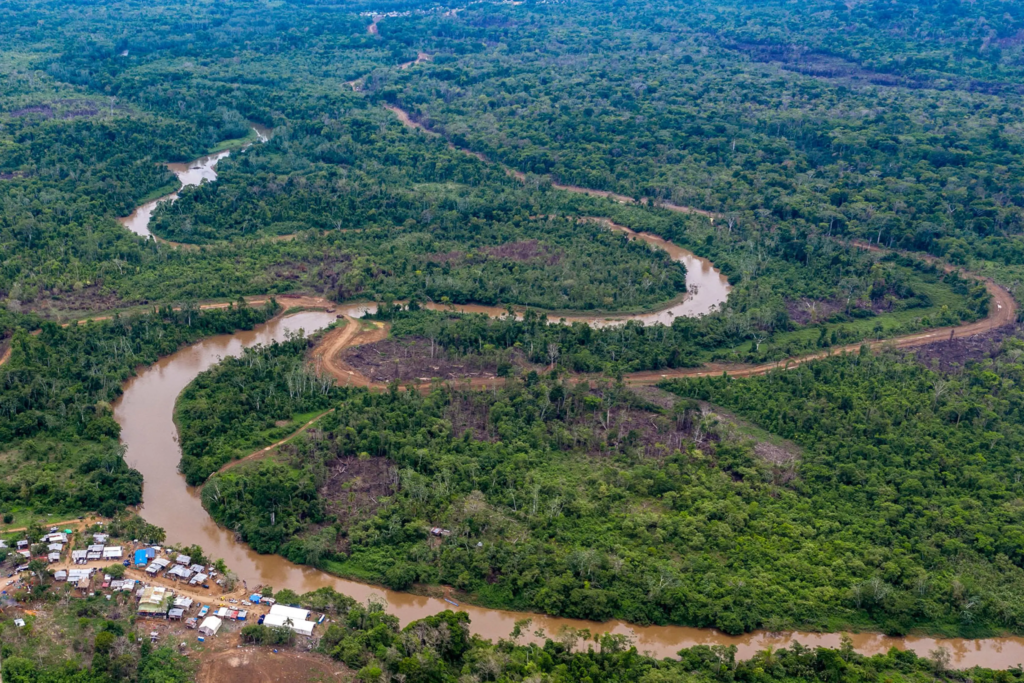

Meanwhile, Central and South American governments face pressure to address the crisis within their borders. Panama has attempted to regulate migration flows by increasing patrols and checkpoints, while Colombia has pledged to crack down on smuggling networks.
However, enforcement alone cannot solve the problem, as the root causes of migration—poverty, violence, and lack of opportunities—continue to push people toward the perilous journey through the Darien Gap.
The Darien Gap remains one of the most treacherous migration routes in the world, claiming countless lives every year. Despite the extreme dangers, migrants from across the globe continue to risk everything in their pursuit of a better life.
The increasing use of the ‘donkey route’ by Indian migrants and others highlights the desperation that drives people to undertake this perilous journey.
As governments tighten immigration policies, the number of people attempting to cross the Darien Gap is unlikely to decrease unless broader solutions are implemented.
Addressing the root causes of migration, providing safer legal pathways, and enhancing international cooperation are crucial to preventing further loss of life. Until then, the Darien Gap will remain a grim symbol of the global migration crisis, where hope and desperation collide in one of the world’s most dangerous landscapes.

